THE VENTRAL SURFACE : The ventral surface of the sheep brain is home to many important distinguishable structures. Below are some of the major ones and their functions. Some structures were introduced on the previous page. Click  for additional photos. for additional photos.
|
|
Spinal Cord : extends from the brain to make up the rest of the CNS; transmits nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
|
|
|
|
|
Medulla : contains cardiac, respiratory, and vomiting centers; deals with breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and other autonomic functions
|
|
|
|
|
Pons : "the bridge" conducts signals from the cerebrum to the cerebellum and medulla and carries sensory signals up to the thalamus; smaller in the sheep brain than the human brain.
|
|
|
|
|
Cerebellum : responsible for coordination and balance; synthesizes the conjunction of sensory input and motor output.
|
|
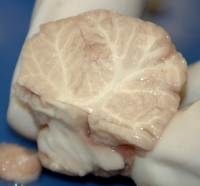
A midsagittal cut of the cerebellum, revealing the grey & white matter inside.
|
|
|
Mammillary Bodies : part of the limbic system; relay impulses from the hippocampus and amygala to the thalamus via the mamillo-thalamic tract.
|
|
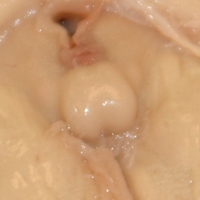
The mammillary bodies up close.
|
|
|
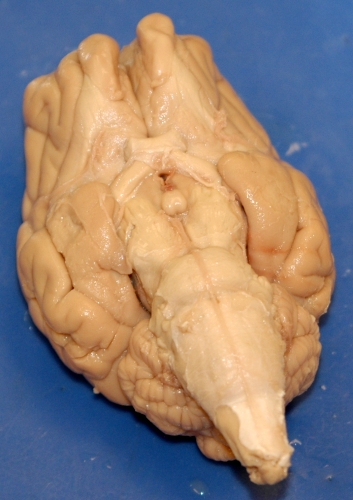
Optic Tracts/Optic Chiasm : the optic nerves are cranial nerves relay informations from the eyes to the brain; the right visual field of each eye crosses the path of the left visual field from each eye through the optic chiasm, making the system contrilateral. On the ventral view, the optic tracts/chiasm are in plain view, but the optic nerves are sliced off.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |


| |
|



